Hemangiomas
Call (877) 900-3223
Hemangiomas
Overview Types of Hemangiomas
Treatment for Hemangiomas
A hemangioma is a birthmark that may appear at birth (congenital hemangioma) or begin growing shortly thereafter. This benign (noncancerous) growth forms due to an abnormal collection of blood vessels, although it is not quite clear why this happens. Nearly 20% of children will develop a hemangioma, and they are more common in Caucasians, twins, females, and premature infants. While they can appear anywhere on the body, hemangiomas most often occur on the face, neck, scalp, chest, or back.
Types of Hemangiomas
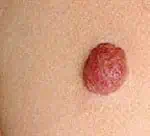
Hemangiomas may be superficial or deep. Superficial hemangiomas, also called capillary hemangiomas or “strawberry hemangiomas,” appear on the surface of the skin as a bright red flat or raised mark, or they may grow into a nodule. A superficial hemangioma is made up of small capillaries that are normal in size and diameter, but high in number.
Deep hemangiomas appear after birth below the skin’s surface, typically on the liver. They are bluish-purple in color and harmless. While some deep hemangiomas make the skin swell and bulge, others may not be visible at all. These are usually detected as an “incidental finding” during an imaging test, such as an ultrasound, MRI, or CT scan. Hemangiomas don’t normally cause symptoms unless they grow large, if there are multiple hemangiomas, or if they grow in a sensitive area. Both types of hemangiomas grow during the first 6-12 months of life, but usually shrink and disappear by the time a child is 5 to 10 years old.
Photo used with permission of the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 2008 Feb;58(2): S16-S22. Copyright Elsevier (2008).
Hemangiomas Treatment
While most hemangiomas are harmless, some may require treatment. If a hemangioma interferes with vision, feeding, breathing, or other body functions, or grows exceptionally large or causes pain, it will likely require treatment by a dermatologist. Treatment methods for superficial hemangiomas may include laser therapy, medication that may include corticosteroids, or surgical removal. Treatment options for deep hemangiomas include surgical removal of the hemangioma or damaged area, or tying off the main artery that supplies blood to the hemangioma. Your dermatologist will advise you whether a hemangioma needs to be treated, as well as the best method of treatment.